|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| addins | ||
| benchmarks | ||
| bin | ||
| config | ||
| docs | ||
| examples | ||
| fpga | ||
| linux | ||
| sim | ||
| src | ||
| studies | ||
| synthDC | ||
| testbench | ||
| tests | ||
| .editorconfig | ||
| .gitattributes | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .gitmodules | ||
| bugs.txt | ||
| CONTRIBUTING.md | ||
| dvtestplan.md | ||
| gitflow.txt | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| Makefile | ||
| README.md | ||
| setup.csh | ||
| setup.imperas.sh | ||
| setup.sh | ||
| wallyriscvTopAll.png | ||
core-v-wally
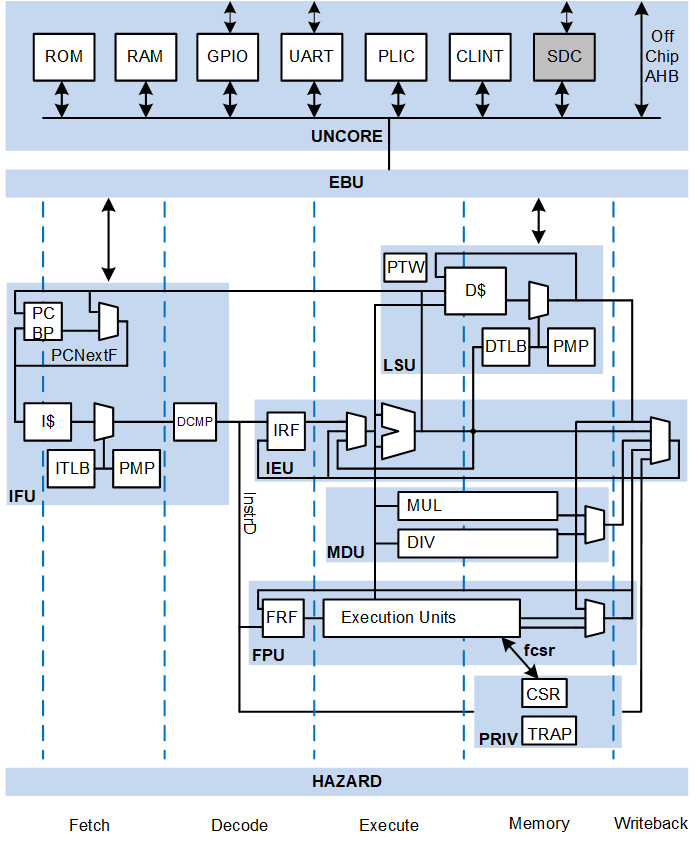
Wally is a 5-stage pipelined processor configurable to support all the standard RISC-V options, incluidng RV32/64, A, C, F, D, Q, M, and Zb* extensions, virtual memory, PMP, and the various privileged modes and CSRs. It provides optional caches, branch prediction, and standard RISC-V peripherals (CLINT, PLIC, UART, GPIO). Wally is written in SystemVerilog. It passes the RISC-V Arch Tests and boots Linux on an FPGA. Configurations range from a minimal RV32E core to a fully featured RV64GC application processor.
Wally is described in an upcoming textbook, RISC-V System-on-Chip Design, by Harris, Stine, Thompson, and Harris. Users should follow the setup instructions below. A system administrator must install CAD tools using the directions further down.
Verification
Wally is presently at Technology Readiness Level 4, passing the RISC-V compatibility test suite and custom tests, and booting Linux in simulation and on an FPGA. See the Test Plan for details.
New User Setup
New users may wish to do the following setup to access the server via a GUI and use a text editor.
Git started with Git configuration and authentication: B.1 (replace with your name and email)
$ git config --global user.name "Ben Bitdiddle"
$ git config --global user.email "ben_bitdiddle@wally.edu"
$ git config --global pull.rebase false
Optional: Download and install x2go - A.1.1
Optional: Download and install VSCode - A.4.2
Optional: Make sure you can log into your server via x2go and via a terminal
Terminal on Mac, cmd on Windows, xterm on Linux
See A.1 about ssh -Y login from a terminal
Then clone the repo, source setup, make the tests and run regression
If you don't already have a Github account, create one
In a web browser, visit https://github.com/openhwgroup/cvw
In the upper right part of the screen, click on Fork
Create a fork, choosing the owner as your github account and the repository as cvw.
On the Linux computer where you will be working, log in
Clone your fork of the repo and run the setup script. Change to your github id.
$ cd
$ git clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/<yourgithubid>/cvw
$ cd cvw
$ git remote add upstream https://github.com/openhwgroup/cvw
$ source ./setup.sh
Add the following lines to your .bashrc or .bash_profile to run the setup script each time you log in.
if [ -f ~/cvw/setup.sh ]; then
source ~/cvw/setup.sh
fi
Edit setup.sh and change the following lines to point to the path and license server for your Siemens Questa and Synopsys Design Compiler installation and license server. If you only have Questa, you can still simulate but cannot run logic synthesis.
export MGLS_LICENSE_FILE=1717@solidworks.eng.hmc.edu # Change this to your Siemens license server
export SNPSLMD_LICENSE_FILE=27020@zircon.eng.hmc.edu # Change this to your Synopsys license server
export QUESTAPATH=/cad/mentor/questa_sim-2021.2_1/questasim/bin # Change this for your path to Questa
export SNPSPATH=/cad/synopsys/SYN/bin # Change this for your path to Design Compiler
If the tools are not yet installed on your server, follow the Toolchain Installation instructions in the section below.
Build the tests and run a regression simulation with Questa to prove everything is installed. Building tests will take a while.
$ make
$ cd sim
$ ./regression-wally (depends on having Questa installed)
Toolchain Installation (Sys Admin)
This section describes the open source toolchain installation. The current version of the toolchain has been tested on Ubuntu and Red Hat/Rocky 8 Linux. Ubuntu works more smoothly and is recommended unless you have a compelling need for RedHat.
Ubuntu users can install the tools by running
$ sudo $WALLY/bin/wally-tool-chain-install.sh
See wally-tool-chain-install.sh for a detailed description of each component, or to issue the commands one at a time to install on the command line.
Installing EDA Tools
Electronic Design Automation (EDA) tools are vital to implementations of System on Chip architectures as well as validating different designs. Open-source and commercial tools exist for multiple strategies and although the one can spend a lifetime using combinations of different tools, only a small subset of tools is utilized for this text. The tools are chosen because of their ease in access as well as their repeatability for accomplishing many of the tasks utilized to design Wally. It is anticipated that additional tools may be documented later after this is text is published to improve use and access.
Siemens Quest is the primary tool utilized for simulating and validating Wally. For logic synthesis, you will need Synopsys Design Compiler. Questa and Design Compiler are commercial tools that require an educational or commercial license.
Note: Some EDA tools utilize LM_LICENSE_FILE for their environmental variable to point to their license server. Some operating systems may also utilize MGLS_LICENSE_FILE instead, therefore, it is important to read the user manual on the preferred environmental variable required to point to a user’s license file. Although there are different mechanisms to allow licenses to work, many companies commonly utilize the FlexLM (i.e., Flex-enabled) license server manager that runs off a node locked license.
Although most EDA tools are Linux-friendly, they tend to have issues when not installed on recommended OS flavors. Both Red Hat Enterprise Linux and SUSE Linux products typically tend to be recommended for installing commercial-based EDA tools and are recommended for utilizing complex simulation and architecture exploration. Questa can also be installed on Microsoft Windows as well as Mac OS with a Virtual Machine such as Parallels.
Siemens Questa
Siemens Questa simulates behavioral, RTL and gate-level HDL. To install Siemens Questa first go to a web browser and navigate to https://eda.sw.siemens.com/en-US/ic/questa/simulation/advanced-simulator/. Click Sign In and log in with your credentials and the product can easily be downloaded and installed. Some Windows-based installations also require gcc libraries that are typically provided as a compressed zip download through Siemens.
Synopsys Design Compiler (DC)
Many commercial synthesis and place and route tools require a common installer. These installers are provided by the EDA vendor and Synopsys has one called Synopsys Installer. To use Synopsys Installer, you will need to acquire a license through Synopsys that is typically Called Synopsys Common Licensing (SCL). Both the Synopsys Installer, license key file, and Design Compiler can all be downloaded through Synopsys Solvnet. First open a web browser, log into Synsopsy Solvnet, and download the installer and Design Compiler installation files. Then, install the Installer
$ firefox &
Navigate to https://solvnet.synopsys.com Log in with your institution’s username and password Click on Downloads, then scroll down to Synopsys Installer Select the latest version (currently 5.4). Click Download Here, agree, Click on SynopsysInstaller_v5.4.run Return to downloads and also get Design Compiler (synthesis) latest version, and any others you want. Click on all parts and the .spf file, then click Download Files near the top move the SynopsysIntaller into /cad/synopsys/Installer_5.4 with 755 permission for cad, move other files into /cad/synopsys/downloads and work as user cad from here on
$ cd /cad/synopsys/installer_5.4
$ ./SynopsysInstaller_v5.4.run
Accept default installation directory
$ ./installer
Enter source path as /cad/synopsys/downloads, and installation path as /cad/synopsys
When prompted, enter your site ID
Follow prompts
Installer can be utilized in graphical or text-based modes. It is far easier to use the text-based installation tool. To install DC, navigate to the location where your downloaded DC files are and type installer. You should be prompted with questions related to where you wish to have your files installed.
The Synopsys Installer automatically installs all downloaded product files into a single top-level target directory. You do not need to specify the installation directory for each product. For example, if you specify /import/programs/synopsys as the target directory, your installation directory structure might look like this after installation:
/import/programs/synopsys/syn/S-2021.06-SP1
Note: Although most parts of Wally, including the software used in this chapter and Questa simulation, will work on most modern Linux platforms, as of 2022, the Synopsys CAD tools for SoC design are only supported on RedHat Enterprise Linux 7.4 or 8 or SUSE Linux Enterprise Server (SLES) 12 or 15. Moreover, the RISC-V formal specification (sail-riscv) does not build gracefully on RHEL7.
The Verilog simulation has been tested with Siemens Questa/ModelSim. This package is available to universities worldwide as part of the Design Verification Bundle through the Siemens Academic Partner Program members for $990/year.
If you want to implement your own version of the chip, your tool and license complexity rises significantly. Logic synthesis uses Synopsys Design Compiler. Placement and routing uses Cadence Innovus. Both Synopsys and Cadence offer their tools at a steep discount to their university program members, but the cost is still several thousand dollars per year. Most research universities with integrated circuit design programs have Siemens, Synopsys, and Cadence licenses. You also need a process design kit (PDK) for a specific integrated circuit technology and its libraries. The open-source Google Skywater 130 nm PDK is sufficient to synthesize the core but lacks memories. Google presently funds some fabrication runs for universities. IMEC and Muse Semiconductor offers full access to multiproject wafer fabrication on the TSMC 28 nm process including logic, I/O, and memory libraries; this involves three non-disclosure agreements. Fabrication costs on the order of $10,000 for a batch of 1 mm2 chips.
Startups can expect to spend more than $1 million on CAD tools to get a chip to market. Commercial CAD tools are not realistically available to individuals without a university or company connection.